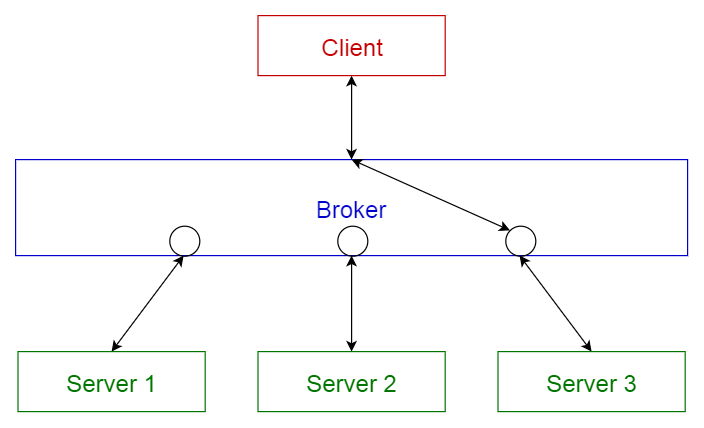
This pattern is used to structure distributed systems with decoupled components. These components can interact with each other by remote service invocations. A broker component is responsible for the coordination of communication among components.
Servers publish their capabilities (services and characteristics) to a broker. Clients request a service from the broker, and the broker then redirects the client to a suitable service from its registry.
Usage
Message broker software such as Apache ActiveMQ, Apache Kafka, RabbitMQ, Websphere MQ and JBoss Messaging.